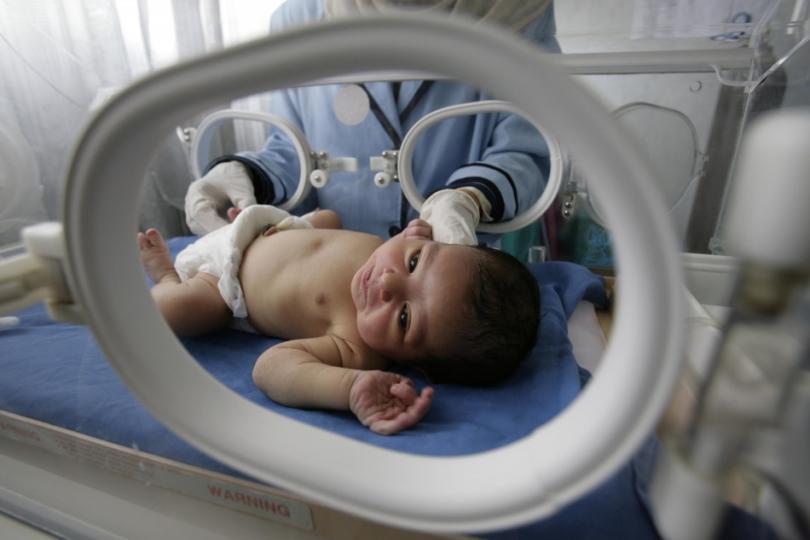
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
When babies are born early, have health problems, or a difficult birth they go to the hospital’s NICU. NICU stands for “neonatal intensive care unit.” There, babies get around-the-clock care from a team of experts.
Most of these babies go to the NICU within 24 hours of birth. How long they stay depends on their health condition. Some babies stay only a few hours or days; others stay weeks or months.
You may hear the NICU called:
- a special care nursery
- an intensive care nursery
- a newborn intensive care nursery
Jaspal Hosptial provides the most sophisticated, technically excellent and highly personalized medical care to children at an affordable cost. Out-Patient Clinics (OPD) are conducted by highly qualified and experienced Consultant. Prepared to undertake routine and complex Paediatrics medical cases round the clock, this department is fully-fledged by automated Lab services and Imaging. Indoor facilities are available 24 hours with a Paediatrician available around the clock and trained nursing staff for managing paediatrics patients.


Reasons Why Your Baby Might Be Sent to the NICU. Prematurity. Babies born early (less than 37 completed weeks) is the most common reason for NICU admission. Premature babies aren’t quite physically and developmentally developed and are unable to transition to the outside environment as well as full-term babies.
- Premature birth is the most common reason a baby is admitted into the NICU. A baby is premature if he or she is born before 37 completed weeks of gestation. Premature babies can experience problems such as low birth weight, unstable vital signs, and irregular temperature. In the NICU, premature babies receive care in a safe, controlled environment. An incubator helps provide the baby with a constant body temperature. These babies are given high-calorie nutrition, intravenous hydration, and other therapies based on any other conditions.
- Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), also called infant respiratory distress syndrome, is a breathing disorder in newborns caused by immature lungs. Babies with mild RDS can be treated by using a machine that pushes air in through the nose to help keep the lungs distended. Babies with severe RDS can be treated with a breathing tube, as well as placing the baby on a ventilator.
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) is usually seen in premature babies, babies born to a mother experiencing gestational diabetes, or infants with an infection.
- Difficult birth can result in decreased blood flow and oxygen to the baby. Should this happen, neonatologists can treat the baby with whole-body cooling, a method to help decrease brain injury that could occur due to decreased blood flow.
- Maternal chorioamnionitis is a condition in which bacteria infect the membranes (chorion and amnion) surrounding the baby, the amniotic fluid, and/or umbilical cord. Bacteria can cause infections in both the mother and fetus. This condition puts a baby at high risk for an infection. After birth, the baby starts on antibiotics to clear the infection.
- Sepsis or infection is more likely in a baby born early than in a full-term baby. Antibiotics may be used based on the type of infection and laboratory tests.
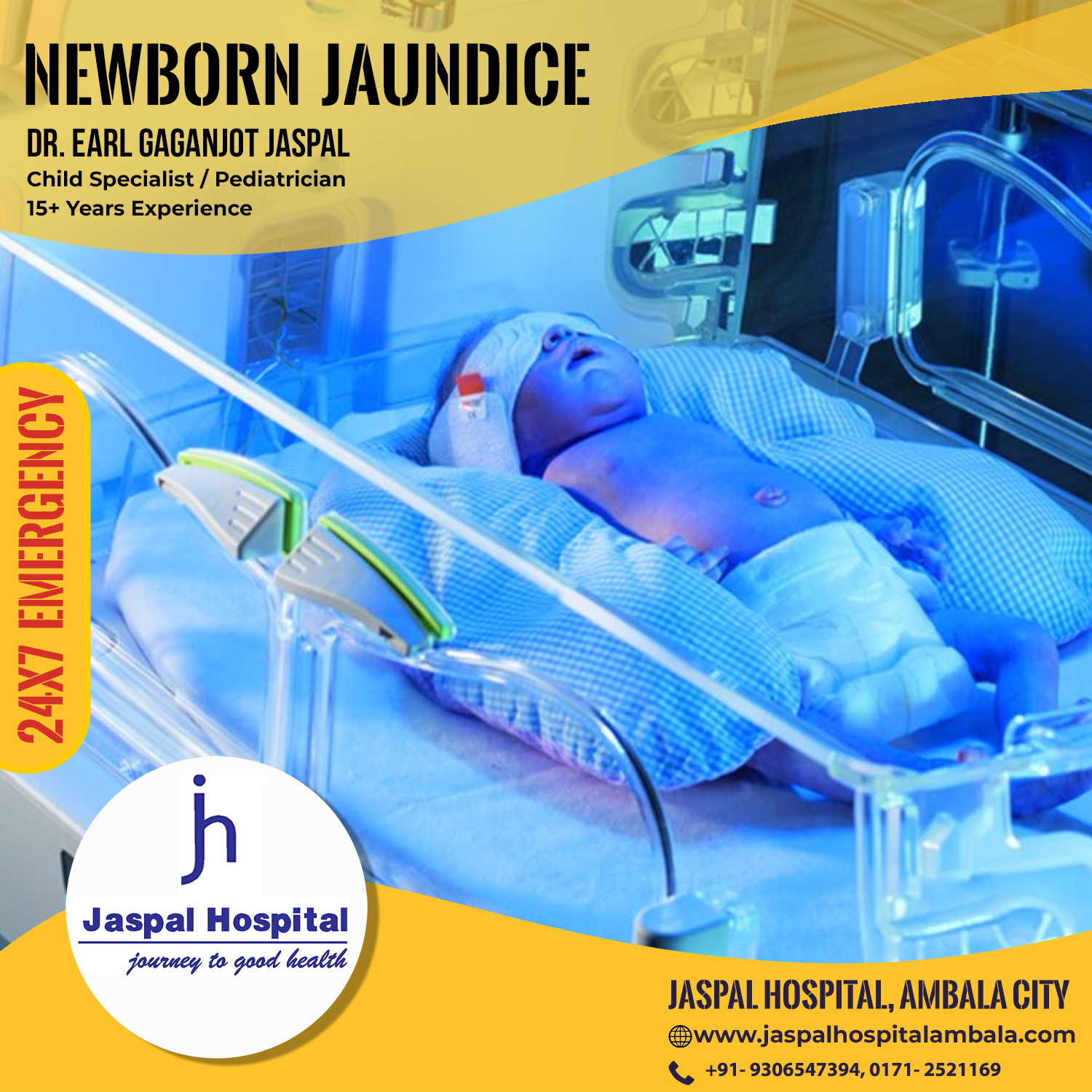
CPAP Treatment
CPAP is a form of treatment in which CPAP machine applies mild continuous air pressure on the lungs through nose to keep small air sacs (alveoli) from collapsing. In NICU it is mainly used in the management of respiratory distress in premature babies in whom alveoli in lungs tend to collapse due to lack of surfactant.


Surfactant
Surfactant is a complex naturally occurring substance made of lipids & proteins that are produced in the lungs. It reduces the surface tension of fluid in the lungs & helps make the small air sacs in the
lungs (alveoli ) stable & keeps them from collapsing when the baby exhales. In preparation for breathing air fetuses begin making surfactant while still in the womb. Babies that are born very prematurely lack adequate surfactant. Due to lack of surfactant lungs of these premature babies start collapsing & baby develop breathing difficulty within a few hours after birth. If a surfactant is administered to these babies soon after birth their chances of survival improve considerably.
Exchange Transfusion
It is a procedure in which aliquots of patient blood are replaced with donor blood in order to remove harmful circulating toxins such as bilirubin. In our set up exchange transfusion is done in babies suffering from severe jaundice when other methods of treatment such as intensive phototherapy have been ineffective. It lowers the serum bilirubin level & reduce the risk of brain damage.